Unpacking The **Bit Of Swiss**: The Tiny Heart Of Our Digital World
Have you ever stopped to think about the absolute smallest pieces of information that make our digital world go 'round? It's a bit like looking at a finely crafted Swiss watch, where every tiny gear plays a huge part. We're talking about something so fundamental, yet so powerful, it truly shapes how we connect, learn, and experience everything online. This tiny, yet incredibly precise, piece of data is what we're calling a "bit of Swiss" knowledge.
You see, every picture you view, every message you send, and every video you stream is built from these microscopic building blocks. It's pretty amazing, actually, how something so small can hold so much importance in our everyday lives. So, you know, it’s worth taking a moment to appreciate it.
Today, we’re going to explore this fundamental concept, the very essence of digital information. We'll peel back the layers to see what this "bit of Swiss" truly means, how it works, and why it's the bedrock of all things digital. It’s a bit like understanding the single thread that holds a whole tapestry together, very important.
- Debbie Cartisano Where Is Steve Cartisano S
- Maureen Kelly Bio Wiki Age Height Family
- Young Thug S Children Know Them All
- Meet Quincy Jones 7 Kids Who Are
- Lee Cruse Wiki Tv Host Age Wife
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is a Bit? The Smallest Digital Piece
- The "Bit" in Action: From Tiny States to Big Data
- A Glimpse into the Past: Who Coined the "Bit"?
- Beyond the Binary: What Comes Before and After a Bit?
- Why is this "Bit of Swiss" So Important?
- Bits as Language: More Than Just Numbers
- Frequently Asked Questions About the Bit of Swiss
What Exactly is a Bit? The Smallest Digital Piece
So, what is a bit, really? Well, it's pretty much the most basic unit of information you can find in computing and, you know, digital communications. Think of it like a tiny, tiny decision point. It’s short for "binary digit," and that's a key part of its story.
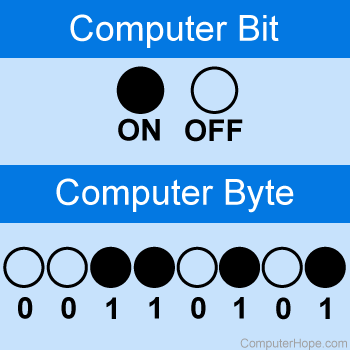
A single bit can only ever hold one of two possible values. It's just like a simple choice, either a 0 or a 1. These two values, 0 and 1, are pretty much the alphabet of the digital world. They represent things like true or false, yes or no, or even, you know, an on or off state. It's that simple, yet incredibly powerful.
A bit is always in one of two physical states. It's very similar to how a light switch works, either completely on or totally off. This state is represented by that single binary value, typically a 0 or a 1. However, these states might also be seen as other pairs, too, like true or false, or even "yes" versus "no."
- Janelle Is Better Youtube Star Detailed Bio
- Utah Ivana Meandzija Missing Or Found Case
- Rapper Lloyd Is A Father Of Two
- Nico Parker Bio Age Career Height Single
- Noah Lalonde Siblings Meet His Sister Emma
How does a computer actually hold onto a bit? Well, it's pretty clever. Bits are stored in memory through the use of capacitors. These tiny components hold electrical charges. The charge, or lack thereof, determines the state of each bit. That, in turn, tells the computer what the bit's value is, whether it’s a 0 or a 1.
Anything with two separate states can actually store one bit in a chip. For example, an electric charge can represent a 0 or a 1 in a hard drive. Or, spots of north or south magnetism can also represent a 0 or a 1. It’s really quite versatile, this little bit.
The "Bit" in Action: From Tiny States to Big Data
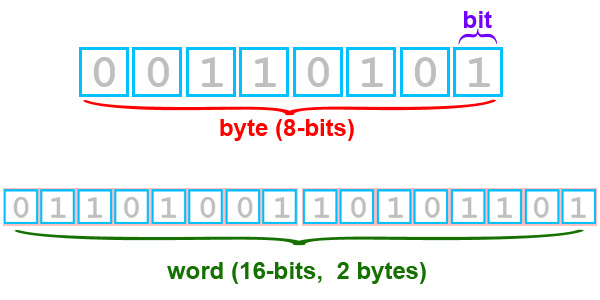
A single bit, by itself, is honestly too small to be much use. It’s like having just one tiny brick. You can't build a house with just one brick, can you? So, what happens is, we group eight bits together. When you do that, you get something called a byte. This is a pretty important step up, you know.
This is why 8 bits make 1 byte. Bytes are the next step up in measuring data. After bytes, we start talking about kilobytes, which are about a thousand bytes. Then there's megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes. These are terms you hear all the time when talking about storage capacity, like for your phone or computer.
While the storage capacity of hard drives is given in bytes, it’s interesting to note that data transfer rates are often shown in bits. So, when your internet speed is advertised as, say, 100 megabits per second, that's bits, not bytes. It’s a subtle but important difference, actually.
The concept of a bit really is the answer to all these questions about how computers handle information. It's the most basic unit of information in computing and, you know, in digital communications. Bits stand for binary digit, as we said, and they are the fundamental building blocks.
Everything in a computer, truly everything, is represented by 0's and 1's. The bit stores just a 0 or a 1. It's the smallest building block of storage there is. It's a pretty remarkable system, actually, how something so simple can create such complex outcomes.
A Glimpse into the Past: Who Coined the "Bit"?
It's always interesting to know where these important terms come from, isn't it? The term "bit" was first used by John Tukey. He was a leading statistician and, apparently, an adviser to five U.S. Presidents. He used the term in a 1946 memo for Bell Labs, which is pretty cool.
This memo, actually, was part of a very important paper that helped start the field of information theory. This academic area, you know, explores how information is quantified and communicated. The concept of entropy, which is a measure of information quantity, used "bit" as its unit. So, it was right there at the very beginning of a whole new way of thinking about data.
Beyond the Binary: What Comes Before and After a Bit?
This is a question people often ask: what comes before a bit? And the simple answer is, well, nothing. A bit is the smallest unit of computer measurement. So, you know, there’s nothing smaller than it in this context. It's the absolute starting point for digital information.
Then, what comes after a bit? After a bit, you get something called a nibble. It’s kind of a fun name, isn't it? A nibble is actually a group of four bits. It's not as commonly talked about as a byte, but it's the next step up from a single bit.
Why is this "Bit of Swiss" So Important?
So, why is this tiny "bit of Swiss" knowledge so important? Well, it represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented as either 1 or 0. But, you know, other representations work too, like true or false, or yes versus no, or even on and off. This flexibility makes it universally useful.
The bit is the foundational element that allows computers to process and store all sorts of data. Every character you type, every pixel on your screen, every sound you hear – it all boils down to these tiny 0s and 1s. It's like the fundamental particle of the digital universe, really.
This concept is so simple, yet so profoundly powerful. It's what makes all our digital devices work. From the smallest calculation to the biggest data centers, it’s all built on the reliable, precise operation of these bits. It’s a bit like the precision of a fine Swiss mechanism, where every tiny part works perfectly to make the whole thing function flawlessly.
The meaning of "bit" also extends beyond just computing. It can mean the biting or cutting edge or part of a tool, for example. Or, you know, a small portion, degree, or amount of something. "A small piece of something often + of" is another way to think about it. It can also refer to a part of something, like a book or a play.
Sometimes, "bits" are basically jokes, but in the context of a play or film, they usually involve a physical element and more than just words. This shows how versatile the word "bit" can be, but when we talk about a "bit of Swiss" in the digital sense, we are squarely focused on that precise, foundational binary digit.
It's the smallest unit of electronic information. Multiple bits form a byte, and then those bytes combine to create the vast amounts of data we see every day. This simple, two-state system is, honestly, the genius behind all digital information. It’s pretty much the backbone of everything.
Bits as Language: More Than Just Numbers
While we often think of bits as 0s and 1s, it's useful to remember they represent a choice between two alternatives. This is what makes them so versatile. They are not just numbers; they are, in a way, the most basic form of communication.
For instance, a single bit can define a boolean value, which is simply true or false. This is a very common concept in programming and logic. It’s how computers make simple decisions. So, you know, it’s a lot more than just a number; it’s a tiny piece of logic.
This foundational simplicity allows for incredible complexity. Imagine building a huge, intricate structure from just two types of LEGO bricks. That's kind of what bits allow us to do in the digital world. It's truly remarkable, actually.
Learn more about data units on our site, and link to this page understanding binary for more insights.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Bit of Swiss
Here are some common questions people often have about the fundamental "bit of Swiss" that underpins our digital lives.
What is the smallest unit of digital information?
The smallest unit of digital information is, you know, the bit. It’s short for "binary digit," and it can hold just one of two values, either a 0 or a 1. It's the absolute tiniest piece of data that a computer can recognize and work with.
Why is a bit called a binary digit?
A bit is called a binary digit because "binary" means "composed of two parts." Since a bit can only have one of two possible values (0 or 1), it perfectly fits the description of a binary system. It’s a pretty straightforward name, actually, once you know what it means.
How does a computer store a bit?
Computers store bits using various physical states that represent the two values. For example, in memory, bits are often stored as electrical charges in capacitors. On a hard drive, they might be stored as tiny spots of magnetism. So, you know, it’s about physical states representing those 0s and 1s.
For a more detailed look at information theory and the origins of the bit, you might find this resource helpful: Britannica's Information Theory Overview.
- Kelly Jones Is Happily Married To His
- Who Is Santhivila Dinesh Wiki Age Bio
- Here S How Much Mia Farrow Is
- Liz Cheney Husband Children Age Net Worth
- Hgtv S Designer David Bromstad Has A
Teach-ICT OCR GCSE Computing - storage sizes and units, bits, bytes

What is binary? - Year 10 Computer Science
How Much is 1 Byte, Kilobyte, Megabyte, Gigabyte, Etc.?